BinPy is a digital electronics simulation library with a bunch of digital devices ( and a few experimental analog devices ) and tools / algorithms under its hood. BinPy is aimed towards students, helping them learn about digital logic in an interactive way. Being an open source project makes it easier for one to get an indepth understanding of the the underlying concepts by glossing at the source.
BinPy focusses on the fundamentals. Everything has been written from scratch such as gates, logical operations, etc.
Our future goals include a GUI tool to help easily build simple digital circuts and the implementation of the core using SPICE or equivalent tools for precise simulations.
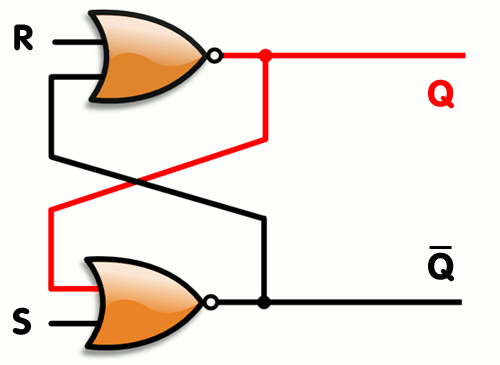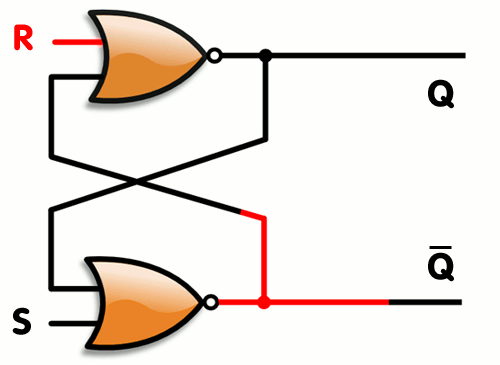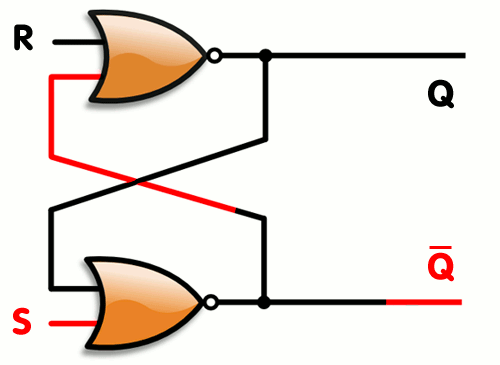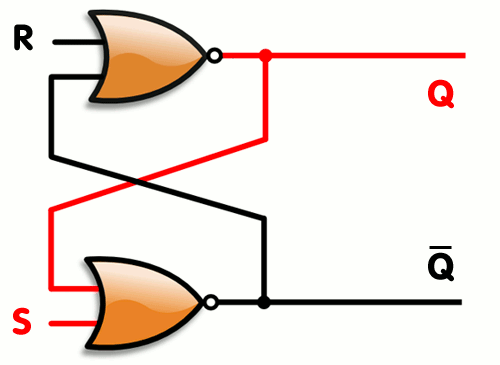
Here's an example of SR latch constructed from a pair of cross-coupled NOR gates
[ Image of SR Latch taken from Wikipedia ]
[ BinPy Code to Simulate an SR Latch ]
from __future__ import print_function
from BinPy import *
# Connector to connect output of second NOR gate with input of first NOR gate
con1 = Connector()
# Connector to connect output of first NOR gate with input of second NOR gate
con2 = Connector()
R = 0 # Reset input for the SR-Latch
S = 0 # Set input for the SR-Lacth
NOR1 = NOR(con1, R) # First NOR gate
NOR1.setOutput(con2) # Set output for NOR gate
NOR2 = NOR(con2, S) # Second NOR gate
NOR2.setOutput(con1) # Set output for NOR gate
NOR1.setInput(1, 1)
NOR2.setInput(1, 0) # Set state
print('Q: ', NOR2.output(), '\t', 'Q\': ', NOR1.output())
NOR1.setInput(1, 0)
NOR2.setInput(1, 1) # Reset state
print('Q: ', NOR2.output(), '\t', 'Q\': ', NOR1.output())
NOR1.setInput(1, 0)
NOR2.setInput(1, 0) # Hold state
print('Q: ', NOR2.output(), '\t', 'Q\': ', NOR1.output())
NOR1.setInput(1, 1)
NOR2.setInput(1, 1) # Invalid state
print('Q: ', NOR2.output(), '\t', 'Q\': ', NOR1.output())
Output
Q: 1 Q': 0
Q: 0 Q': 1
Q: 0 Q': 1
Q: 0 Q': 0 #Invalid StateOperations, Combinatonal Logic and Algorithms
from BinPy import *
# Operations
operator = Operations()
operator.ADD(1011,11)
operator.SUB(1011,11)
operator.COMP('0011',1) #Second argument chooses betweem 1's or 2's Compliment
# Combinational Logic
m = MUX(1,1,0,1)
m.selectLines(0,1)
print "MUX Out: ", m.output()
d = DEMUX()
d.selectLines(0,1)
print "DEMUX Out: ", d.output()
d = Decoder(0,1)
print "Decoder Out: ", d.output()
e = Encoder(0,1,0,0)
print "Encoder Out: ", e.output()
# Sequential Circuits
a = DFlipFlop(1,0)
print "DFlipFlop Out: ", a.output()
# IC
myIC = IC_7400()
p = {1:1,2:0,4:0,5:0,7:0,10:1,9:1,13:0,12:0,14:1}
myIC.setIC(p)
print "IC_7400 Out: ", myIC.run()
myIC1 = IC_7401()
p = {2:0,3:1,5:0,6:0,7:0,8:1,9:1,11:0,12:0,14:1}
myIC1.setIC(p)
print "IC_7401 Out: ", myIC1.run()
# Algorithms
# Includes the Quine-McCluskey algorithm for solving K-Maps
FinalEquation = QM(['A','B'])
print "Minimized Boolean Equation : " , FinalEquation.get_function(qm.solve([0,1,2],[])[1])Output
{'carry': 0, 'sum': [1, 1, 1, 0]}
{'carry': 1, 'difference': [1, 0, 0, 0]}
MUX Out: 1
DEMUX Out: [0, 0, 0, 0]
Decoder Out: [0, 1, 0, 0]
Encoder Out: [0, 1]
DFlipFlop Out: [1,0]
IC_7400 Out: {8: 0, 11: 1, 3: 1, 6: 1}
IC_7401 Out: {1: 1, 10: 0, 4: 1, 13: 1}
Minimized Boolean Equation : ((NOT B) OR (NOT A))BinPy also comes with a console that is a simple wrapper around the classic python console from which you can directly use the BinPy Resources.
To start it, simply issue $ binpy if BinPy is installed in your path.
Auto-generated documentation is available for reference at BinPy docs
Check out the BinPy Wiki page for a complete summary of BinPy, The Development workflow, Downloading and Installation guide, Tutorials, Technical References and Much more.
###Install with pip
#####Python2
######PIP and setuptools
sudo apt-get install python-pip
sudo pip install --upgrade setuptools######BinPy
sudo pip install https://github.com/BinPy/BinPy/zipball/master######IPython Notebook
sudo pip install --upgrade ipython[all]#####Python3
######PIP and setuptools
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
sudo pip3 install --upgrade setuptools######BinPy
sudo pip3 install https://github.com/BinPy/BinPy/zipball/master######IPython Notebook
sudo pip3 install --upgrade ipython[all]#####Install autopep8 Tool to ensure your contributions pass the pep8 test.
sudo pip install --upgrade autopep8###Install BinPy using git
#####Python2
sudo apt-get install git setuptools
git clone https://github.com/BinPy/BinPy.git
cd BinPy/
sudo python setup.py install#####Python3
sudo apt-get install git python3-pip
sudo pip3 install --upgrade setuptools
git clone https://github.com/BinPy/BinPy.git
cd BinPy/
sudo python3 setup.py install- Introduction of all ICs
- Introduction of problem solving algorithms
- Addition of Microprocessors and Analog Devices
- Graphical representation of the circuit
Visit our roadmap and ideas page in Wiki to know more.
For a detailed summary of all the coding guidelines and development workflow, visit our Wiki page.
- Report Bugs and Issues
- Solve Bugs and Issues
- Write Tutorials, Examples and Documentation
DEV NOTE:
-
It is expected that your code must follow pep8 standards. To conform to the same please install
autopep8tool following the instructions in the installation section. -
After installation is complete. Make the necessary changes and commit your changes. After Committing your changes,
cdto the BinPy root directory and issue the following commandautopep8 -r -i -a -a -v .To learn more about the
autopep8tool visit here. -
Ensure that all the tests pass by running
nosetests; nosetests3inBinPy\BinPy\testsdirectory. -
To check for the pep8 indentation status issue the following command
pep8 ./ --ignore=E501
If all the tests pass successfully push your repo to the origin/branch and send us a Pull Request. We'll be happy to review the same and merge it with our codebase.