HMS Malabar (1804)
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | Cuvera |
| Namesake | Hindu god of wealth |
| Owner | Lambert, Ross, & Co. |
| Builder | Calcutta |
| Launched | 12 September 1798 |
| Fate | Sold 30 May 1804 |
| Name | HMS Malabar |
| Namesake | Malabar Coast |
| Acquired | 30 May 1804 |
| Renamed | HMS Coromandel on 7 March 1815 |
| Reclassified |
|
| Fate | Broken up in December 1853 |
| General characteristics [1] | |
| Class and type | 56-gun fourth rate |
| Tons burthen | 93556⁄94, or 93562⁄94[2] (bm) |
| Length |
|
| Beam | 37 ft 2 in (11.3 m) |
| Propulsion | Sails |
| Sail plan | Full-rigged ship |
| Complement |
|
| Armament |
|
HMS Malabar was a 56-gun fourth rate of the Royal Navy. She had previously been the East Indiaman Cuvera, launched at Calcutta in 1798. She made one voyage to London for the British East India Company and on her return to India served as a transport and troopship to support General Baird's expedition to Egypt to help General Ralph Abercromby expel the French there. The Navy bought her in 1804 and converted her to a storeship in 1806. After being renamed HMS Coromandel she became a convict ship and made a trip carrying convicts to Van Diemen's Land and New South Wales in 1819. She spent the last 25 years of her career as a receiving ship for convicts in Bermuda before being broken up in 1853.
East Indiaman
[edit]Malabar was originally built as the East Indiaman Cuvera at Calcutta in 1798.[a] She was a two-decker vessel built of teak from Pegue.[5]
Cuvera made one round trip to England and back under Captain John Lowe. Cuvera was at Calcutta on 19 November 1798. She left Calcutta on 12 January, and passed Saugor on 28 January 1799. She left Bengal on 10 February, and reached St Helena on 10 May.[4] She arrived at London on 26 July, with 2313 bales of cotton from Bengal.[6] She also carried one French officer who had been taken prisoner in the Nizam's service in 1798. For this service she earned passage money of Rs 1,000.[7]
Because she sailed in wartime, i.e., during the French Revolutionary Wars, in England Captain John Lowe applied for and received a letter of marque, which was dated 5 December 1799.[3] Acquiring a letter of marque was usual practice for captains in the EIC's service as it authorised them to engage in offensive action against the French, or their allies, and not just defend themselves. Cuvera was admitted to the Registry of Great Britain on 27 November 1799.[2]
She left England on 15 February 1800 for the Cape and Bengal,[6] carrying a cargo for the British government. When she left England she was in company with Carron, Scaleby Castle, and Minerva. She left Fort St George for Bengal on 4 September 1800.
The East India Company then chartered her out as a transport and troopship to support Baird's expedition to Egypt to help General Ralph Abercromby expel the French there. The charter for Cuvera was Rs.14,000 per month.[8] Payments included Rs. 70,000 for five months from 31 December 1800 to April 1801, and Rs. 16,000 to Lowe in consideration of his ship "being diverted from its original destination to the Transport Service",[9] Rs 168,000 for 12 months charter from 31 March 1801,[10] and Rs. 94,987 for charter to 23 October 1802.[11]
On 23 May 1801, Sir Home Popham drew 6,000 Spanish dollars for His Majesty's ships on the expedition from the treasury on Cuvera, while she was in the Judda road.[12]
Lowe later also received £328 for
...sundry presents given to Johnnie Katcheef, of Keree, and Teregah Aga, at Cossire, to interest them in the safe conduct of dispatches sent to Commodore Sir Home Popham, K.M. Mr Melville, and establishment passing the desert, and for the protection of the bakers, &c. &c. working on shore, as well as to the sick landed at Cossire.[13]
Baird landed at Kosseir (or Cossire), on the Egyptian side of the Red Sea. He then led his troops army across the desert to Kena on the Nile, and then to Cairo. He arrived before the battle of Alexandria in time for the final operations.[14]
General Arthur Wellesley had appointed Lowe agent for the transports at Rs 1000 per month. He received Rs. 9580 10 annas 3 pice for his service from January to 18 October 1802.[15]
HMS Malabar
[edit]The Admiralty purchased Cuvera from the East India Company on 30 May 1804 for £19,719 and renamed her Malabar.[1][b] Barnard & Co., of Deptford fitted her out in June to July 1804 before the Deptford Dockyard completed the work in December. She was commissioned in July 1804 under Captain George Byng.[1]
In 1805 she sailed for the West Indies under Captain Robert Hall.[1] On 2 January 1806 she and the brig-sloop Wolf, (or Wolfe), Captain George Charles Mackenzie, captured the French privateer schooners Régulateur and Napoléon in Port Azarades, Cuba. The port was protected by a double reef of rocks so Hall sent the master of Malabar in a boat to find a passage. Once a passage was found, rather than go in to capture the vessels, Wolfe came in, but stopped about a quarter of a mile away. She then engaged the privateers for almost two hours until their crews abandoned their vessels, landed, and escaped into the woods. Then Wolfe and Malabar sent in their boats to take possession.[16]
Régulateur was armed with a brass 18-pounder and four 6-pounder guns, and had a crew of 80 men.[16] Napoléon was armed with a long 9-pounder gun, two 12-pounder carronades and two 4-pounder guns, and had a crew of 66 men.[16] The British captured only four men, one of whom was mortally wounded. Malabar lost one man drowned when Régulateur sank while being towed out past the reefs; two prisoners also died at this time. Wolf lost two men killed and four wounded.[16] Later accounts give the name of the ship that sank as Brutus.[c]
Malabar sailed under Captain George Scott in March 1806 and then James Aycough in July.[1] From November 1806 to January 1807 Malabar was in Woolwich being fitted as a 20-gun storeship. In November 1806 she was commissioned under Captain John Temple, and after fitting out sailed for the North Sea.[1]
At a court martial on board Gladiator at Portsmouth on 1 June 1807, Lieutenant Pennyman Stevenson of Malabar was found guilty of neglect of duty and dismissed from the Navy.[18] Malabar sailed for the River Plate later that month.[19]
Malabar was commissioned in May 1808 under J. Henzell (Master).[1] Lloyd's List reported on 10 May 1808 that the Portuguese brig Legeiro had arrived at Portsmouth. Legeiro, Ramos, master, had been sailing from Bengal to Lisbon when the man-of-war Malabar had detained her.[20]
After again fitting out as a storeship in July–August 1808, Malabar was commissioned under F. Bradshaw (master) and served in the Mediterranean from 1809 to 1815.[1]
Still, on 19 December 1809 she sailed from Portsmouth as one of the escorts to the fleet of merchantmen sailing to the West Indies.[21] On 8 June 1810 she was at sea, serving as one of the escorts to the fleet returning from Jamaica.[22]
HMS Coromandel
[edit]On 3 July 1815 Malabar was renamed Coromandel.[1][d] She was again fitted between July and September 1818.[1]
Then between August and October 1819 she and Dromedary were fitted as a convict transports for a voyage to New South Wales. Coromandel also had a raft port cut into her side at Plymouth to enable her to take on lumber. This port would leak on her way out.[23]
Under the command of Captain James Downie, she arrived in Hobart on 12 March 1820 with 300 convicts, as well as detachments of the 46th and the 84th Regiment of Foot. She left half of her complement of prisoners and soldiers in Hobart Town and the remainder sailed on to Sydney, arriving on 5 April.[24] At Sydney both Dromedary and Coromandel were fitted out to carry lumber. They then went their separate ways to New Zealand, Dromedary to Whangaroa and Coromandel to the river Thames.[23]
In New Zealand, Coromandel acquired timber spars for the Royal Navy and undertook coastal survey work.[25] She gave her name to the town Coromandel on the harbour where she stopped to purchase kauri wood for spars, and to the Coromandel Peninsula on which the town sits. Coromandel returned to Sydney in June 1821 and departed again for Britain on 25 July 1821.[26]
Prison hulk
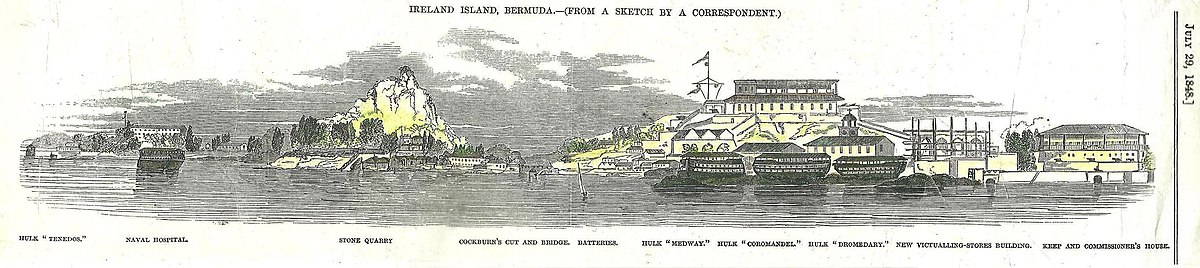
[edit]Coromandel was laid up at Portsmouth in December 1821.[1] She was converted to a receiving ship in June–July 1827. Thereafter she served as a prison hulk at the Royal Naval Dockyard on the island of Ireland, in the Imperial fortress colony of Bermuda from 1828 until 1853.[e] On 12 September 1839, she was driven ashore and severely damaged in a hurricane at Ireland Island, Bermuda. Damage was confined to her starboard side.[27] Coromandel was broken up in 1853 by Admiralty Order.
Notes
[edit]- ^ The summary at the British Library of Cuvera's history gives her launch year as 1796.[4]
- ^ There had been an earlier Malabar, also an East Indiaman, in this case Royal Charlotte, which had foundered in 1796.
- ^ The prize money for an ordinary seamen was 8s 7d.[17]
- ^ The National Maritime Museum database gives the date as 3 March 1813.[19]
- ^ Coromandel was anchored near Dromedary, herself also a converted Indiaman.
Citations
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Winfield (2008), p. 113.
- ^ a b House of Commons (1814), p. 86.
- ^ a b c "Letter of Marque, 1793-1815; p.57". Archived from the original on 9 July 2015. Retrieved 10 August 2011.
- ^ a b British Library: Cuvera.
- ^ Symes (1800), p. 458.
- ^ a b Henchman (1802), Appendices pp.3 & 25.
- ^ The Asiatic annual register or a view of the history of Hindustan and of the politics, commerce and literature of Asia. (1807; Vol. 7), p.114.
- ^ Anon. (1809), p.193.
- ^ The Asiatic Annual Register Or a View of the History of Hindustan and of the Politics, Commerce and Literature of Asia. (London, D Brett) 1801-12, p.145.
- ^ The Asiatic Annual Register Or a View of the History of Hindustan and of the Politics, Commerce and Literature of Asia. (London, D Brett) 1801-12, p.148.
- ^ The Asiatic Annual Register Or a View of the History of Hindustan and of the Politics, Commerce and Literature of Asia. (London, D Brett) 1801-12, p.152.
- ^ The Asiatic Annual Register Or a View of the History of Hindustan and of the Politics, Commerce and Literature of Asia. (London, D Brett) 1801-12, p.153.
- ^ The Asiatic annual register or a view of the history of Hindustan and of the politics, commerce and literature of Asia. (1807; Vol. 7), p.151.
- ^ Chisolm (1911).
- ^ The Asiatic annual register or a view of the history of Hindustan and of the politics, commerce and literature of Asia. (1807; Vol. 7), p.153.
- ^ a b c d "No. 15904". The London Gazette. 25 March 1806. pp. 387–388.
- ^ "No. 15993". The London Gazette. 20 January 1807. p. 80.
- ^ Naval Chronicle (Jan-Jun 1807), Vol. 17, p.510.
- ^ a b "NMM, vessel ID 370832" (PDF). Warship Histories, vol ii. National Maritime Museum. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2011. Retrieved 30 July 2011.
- ^ Lloyd's List №4251.
- ^ Lloyd's List №4329.
- ^ Lloyd's List №4368.
- ^ a b Monin (2001), p. 49.
- ^ Nicholson (1983), p. 59.
- ^ "HMS Coromandel". Early shipping in New Zealand waters. Archived from the original on 10 November 2013. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ^ Cumpston (1977), pp. 121 & 127.
- ^ "Dreadful Hurricane at Bermuda". Caledonian Mercury. No. 18695. Edinburgh. 7 November 1839.
References
[edit]- Anon. (1809) Reports and Papers on the Impolicy of Employing Indian Built Ships in the Trade of the East-India Company, and of Admitting Them to British Registry: With Observation on Its Injurious Consequences to the Landed and Shipping Interests, and to the Numerous Branches of Trade Dependent on the Building and Equipment of British-built Ships. (Blacks and Parry).
- Cumpston, J. L. (1977). Shipping Arrivals & Departures Sydney, 1788-1825. Canberra: Roebuck.
- Henchman, Thomas (1802) Observations on the Reports of the Directors of the East India Company, Respecting the Trade Between India and Europe: To which is Added, an Appendix Containing the Papers Referred to in the Work. (T. Gillet).
- House of Commons, Parliament, Great Britain (1814). Minutes of the Evidence Taken Before the Select Committee on Petitions Relating to East-India-Built Shipping. H.M. Stationery Office.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Monin, Paul (2001). This is My Place: Hauraki Contested, 1769-1875. Bridget Williams Books. ISBN 9781877242199.
- Nicholson, I. H. (1983). Shipping Arrivals & Departures Tasmania 1803-1833. Canberra: Roebuck.
- Symes, Michael (1800). An Account of an Embassy to the Kingdom of Ava, Sent by the Governor-General of India in the Year 1795. Vol. 2. Nicol.
- Winfield, Rif (2008). British Warships in the Age of Sail 1793–1817: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates. Seaforth Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-246-7.
This article includes data released under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported UK: England & Wales Licence, by the National Maritime Museum, as part of the Warship Histories project.