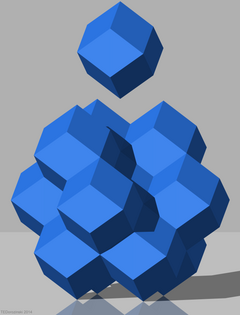
Rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb
| Rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb | |
|---|---|

| |
| Type | convex uniform honeycomb dual |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | |
| Cell type |  Rhombic dodecahedron V3.4.3.4 |
| Face types | Rhombus |
| Space group | Fm3m (225) |
| Coxeter notation | ½, [1+,4,3,4] , [4,31,1] ×2, <[3[4]]> |
| Dual | tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb |
| Properties | edge-transitive, face-transitive, cell-transitive |
The rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb (also dodecahedrille) is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It is the Voronoi diagram of the face-centered cubic sphere-packing, which has the densest possible packing of equal spheres in ordinary space (see Kepler conjecture).
Geometry
[edit]It consists of copies of a single cell, the rhombic dodecahedron. All faces are rhombi, with diagonals in the ratio 1:√2. Three cells meet at each edge. The honeycomb is thus cell-transitive, face-transitive, and edge-transitive; but it is not vertex-transitive, as it has two kinds of vertex. The vertices with the obtuse rhombic face angles have 4 cells. The vertices with the acute rhombic face angles have 6 cells.
The rhombic dodecahedron can be twisted on one of its hexagonal cross-sections to form a trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron, which is the cell of a somewhat similar tessellation, the Voronoi diagram of hexagonal close-packing.

|
 The honeycomb can be derived from an alternate cube tessellation by augmenting each face of each cube with a pyramid. |
 The view from inside the rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb. |
Colorings
[edit]The tiling's cells can be 4-colored in square layers of 2 colors each, such that two cells of the same color touch only at vertices; or they can be 6-colored in hexagonal layers of 3 colors each, such that same-colored cells have no contact at all.
| 4-coloring | 6-coloring |
|---|---|

|

|
| Alternate square layers of yellow/blue and red/green | Alternate hexagonal layers of red/green/blue and magenta/yellow/cyan |
Related honeycombs
[edit]The rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb can be dissected into a trigonal trapezohedral honeycomb with each rhombic dodecahedron dissected into 4 trigonal trapezohedrons. Each rhombic dodecahedra can also be dissected with a center point into 12 rhombic pyramids of the rhombic pyramidal honeycomb.
Trapezo-rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb
[edit]| Trapezo-rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb | |
|---|---|

| |
| Type | convex uniform honeycomb dual |
| Cell type | trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron VG3.4.3.4
|
| Face types | rhombus, trapezoid |
| Symmetry group | P63/mmc |
| Dual | gyrated tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb |
| Properties | edge-uniform, face-uniform, cell-uniform |
The trapezo-rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb is a space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space. It consists of copies of a single cell, the trapezo-rhombic dodecahedron. It is similar to the higher symmetric rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb which has all 12 faces as rhombi.
Related honeycombs
[edit]It is a dual to the vertex-transitive gyrated tetrahedral-octahedral honeycomb.
Rhombic pyramidal honeycomb
[edit]| Rhombic pyramidal honeycomb | |
|---|---|
| (No image) | |
| Type | Dual uniform honeycomb |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagrams | |
| Cell | rhombic pyramid |
| Faces | Rhombus Triangle |
| Coxeter groups | [4,31,1], [3[4]], |
| Symmetry group | Fm3m (225) |
| vertex figures | |
| Dual | Cantic cubic honeycomb |
| Properties | Cell-transitive |
The rhombic pyramidal honeycomb or half oblate octahedrille is a uniform space-filling tessellation (or honeycomb) in Euclidean 3-space.
This honeycomb can be seen as a rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb, with the rhombic dodecahedra dissected with its center into 12 rhombic pyramids.
 rhombic dodecahedral honeycomb |
 Rhombohedral dissection |
 Within a cube |
Related honeycombs
[edit]It is dual to the cantic cubic honeycomb:
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- Williams, Robert (1979). The Geometrical Foundation of Natural Structure: A Source Book of Design. Dover Publications, Inc. p. 168. ISBN 0-486-23729-X.