Portal:Outer space

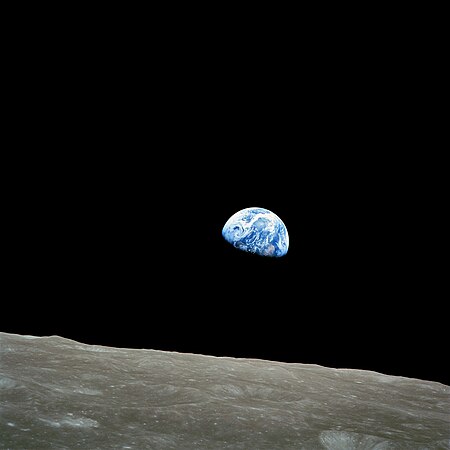
Outer space (or simply space) is the expanse that exists beyond Earth's atmosphere and between celestial bodies. It contains ultra-low levels of particle densities, constituting a near-perfect vacuum of predominantly hydrogen and helium plasma, permeated by electromagnetic radiation, cosmic rays, neutrinos, magnetic fields and dust. The baseline temperature of outer space, as set by the background radiation from the Big Bang, is 2.7 kelvins (−270 °C; −455 °F).
The plasma between galaxies is thought to account for about half of the baryonic (ordinary) matter in the universe, having a number density of less than one hydrogen atom per cubic metre and a kinetic temperature of millions of kelvins. Local concentrations of matter have condensed into stars and galaxies. Intergalactic space takes up most of the volume of the universe, but even galaxies and star systems consist almost entirely of empty space. Most of the remaining mass-energy in the observable universe is made up of an unknown form, dubbed dark matter and dark energy.
Outer space does not begin at a definite altitude above Earth's surface. The Kármán line, an altitude of 100 km (62 mi) above sea level, is conventionally used as the start of outer space in space treaties and for aerospace records keeping. Certain portions of the upper stratosphere and the mesosphere are sometimes referred to as "near space". The framework for international space law was established by the Outer Space Treaty, which entered into force on 10 October 1967. This treaty precludes any claims of national sovereignty and permits all states to freely explore outer space. Despite the drafting of UN resolutions for the peaceful uses of outer space, anti-satellite weapons have been tested in Earth orbit.
The concept that the space between the Earth and the Moon must be a vacuum was first proposed in the 17th century after scientists discovered that air pressure decreased with altitude. The immense scale of outer space was grasped in the 20th century when the distance to the Andromeda galaxy was first measured. Humans began the physical exploration of space later in the same century with the advent of high-altitude balloon flights. This was followed by crewed rocket flights and, then, crewed Earth orbit, first achieved by Yuri Gagarin of the Soviet Union in 1961. The economic cost of putting objects, including humans, into space is very high, limiting human spaceflight to low Earth orbit and the Moon. On the other hand, uncrewed spacecraft have reached all of the known planets in the Solar System. Outer space represents a challenging environment for human exploration because of the hazards of vacuum and radiation. Microgravity has a negative effect on human physiology that causes both muscle atrophy and bone loss. (Full article...)
Io is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter and, with a diameter of 3,642 kilometres (2,263 mi), the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System. It was named after the mythological character of Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of the lovers of Zeus. With over 400 active volcanoes, Io is the most geologically active object in the Solar System. This extreme geologic activity is the result of tidal heating from friction generated within Io's interior as it is pulled between Jupiter and the other Galilean satellites—Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Several volcanoes produce plumes of sulfur and sulfur dioxide that climb as high as 500 km (300 mi) above the surface. Io's surface is also dotted with more than 100 mountains that have been uplifted by extensive compression at the base of the moon's silicate crust. Some of these peaks are taller than Earth's Mount Everest. Unlike most satellites in the outer Solar System, which are mostly composed of water-ice, Io is primarily composed of silicate rock surrounding a molten iron or iron sulfide core. Most of Io's surface is characterized by extensive plains coated with sulfur and sulfur dioxide frost. Io's volcanism is responsible for many of the satellite's unique features. Its volcanic plumes and lava flows produce large surface changes and paint the surface in various shades of yellow, red, white, black, and green, largely due to allotropes and compounds of sulfur. Numerous extensive lava flows, several more than 500 km (300 mi) in length, also mark the surface. The materials produced by this volcanism provide material for Io's thin, patchy atmosphere and Jupiter's extensive magnetosphere. Io's volcanic ejecta also produce a large plasma torus around Jupiter.

- ... that, for the Space 220 Restaurant, Disney reached out to NASA engineers to understand what a space elevator might look like?
- ... that some severe environmental impacts of the invasion of Ukraine can be seen from space?
- ... that the space industry of India has supported the launch of more than 100 domestic satellites and more than 300 foreign satellites?
- ... that Nature's Fynd, producer of microbe-based meat substitutes, is working with NASA to develop a bioreactor for use in space travel?
- ... that Louis W. Roberts was among the highest ranking African-American space program staff at NASA while the Apollo program was underway?
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus