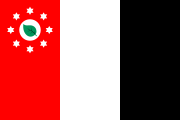
Torres Strait Islander flag
 | |
| Proportion | 2:3 or 1:2 (here) |
|---|---|
| Adopted | 14 July 1995 |
| Designed by | Bernard Namok |
The Torres Strait Islander Flag is an official flag of Australia, and is the flag that represents Torres Strait Islander people. It was designed in 1992 by Bernard Namok. It won a local competition held by the Islands Coordinating Council, and was recognised by the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Commission in June 1992.
Status
The Government of Australia granted it Flag of Australia status, under the Flags Act 1953 (Cth), by proclamation on 14 July 1995.[1]
Due to an "administrative oversight", the 1995 proclamation was not lodged so that it would continue in force indefinitely; hence it automatically expired on 1 January 2008. It was therefore almost identically replaced, on 25 January 2008, with effect as from 1 January.[2]
In the 2008 proclamation, the flag "is recognised as the flag of the Torres Strait Islander people of Australia and a flag of significance to the Australian nation generally" and appointed "to be the flag of the Torres Strait Islander people of Australia and to be known as the Torres Strait Islander Flag". The design is reproduced in Schedule 1 and described in Schedule 2.
Although Namok has since died, the Torres Strait Islander Flag is still subject to copyright under the Copyright Act 1968 (Cth). The copyright was administered by the Island Coordinating Council until 2008, when that body was superseded by the Torres Strait Island Regional Council, which is willing to permit reproductions of the flag that are accurate and that acknowledge Namok as the designer.[3]
Colours
The official colours of the flag of the Torres Strait Islanders are as follows:
| Scheme | Green | Blue | Black | White | Source(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pantone | 3288 C or 342 C | 301 C or 280 C | Black C | Safe | [4][5] |
| RGB
(Hex) |
0–153–102
(#009966) |
0–0–153
(#000099) |
0–0–0
(#000000) |
255–255–255
(#FFFFFF) |
[4] |
| CMYK | 100%–0%–80%–40% | 100%–70%–0%–0% | 0%–0%–0%–100% | 0%–0%–0%–0% | [4] |
Symbolic meaning
The green panels at the top and the bottom of the flag symbolise the land, while the blue panel in the centre represents the waters of the Torres Strait. The thin black stripes between the green and blue panels signify the Torres Strait Islanders themselves. The white five-pointed star at the centre of the flag represents the five major island groups—the Western, Eastern, Central, Port Kennedy and (N.P.A.) Mainland—and the white dhari (also spelt dari, a ceremonial dancer's headdress[6]), around it also symbolises the Torres Strait Islands people. White symbolises peace, while the star is a symbol for navigation.[5]
Public display

The Torres Strait Islander flag is permanently flown alongside the Aboriginal flag in front of Adelaide Town Hall in Adelaide, South Australia.[7]
Following the 2022 Australian federal election on 21 May 2022, the incoming Anthony Albanese-led Labor government started displaying the Aboriginal flag and the Torres Strait Islander flag alongside the national flag at ministerial press conferences.[8] Upon the opening of the new Parliament, both flags began to be displayed in the House of Representatives and Senate chambers.[9]
From 27 May 2022, at the start of National Reconciliation Week, both the Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander flags were hoisted on the front lawn of Government House, Adelaide, to be permanently flown alongside the national flag and the South Australian flag.[10]
Local flags
-
Flag of Murray Island
-
Flag of Saibai Island
See also
References
- ^ Commonwealth of Australia Gazette, Special, No. S 258, 14 July 1995. This was a special issue of the Gazette, printed in colour on high quality paper. It may be found at the back of Government Notices issue No. GN 28, 19 July 1995, together with the proclamation (No. S 259) of the Australian Aboriginal Flag.
- ^ "Flags Act 1953—Proclamation (Australian Aboriginal Flag)". ComLaw. Archived from the original on 17 September 2012. Retrieved 31 May 2014. The only significant change from 1995 is that "Torres Strait Islander flag" is altered to "Torres Strait Islander Flag".
- ^ "Torres Strait Islander flag". Torres Strait Island Regional Council. Archived from the original on 13 July 2018. Retrieved 13 July 2018.
- ^ a b c Australia. (2002). Style manual for authors, editors and printers. Snooks & Co. (6th ed.). Canberra: John Wiley & Sons Australia. p. 300. ISBN 9780701636487. OCLC 49316140.
- ^ a b Cabinet, Prime Minister and (27 June 2016). "Australian flags". www.pmc.gov.au. Archived from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 19 November 2017.
- ^ Whitford, Maddie (13 April 2020). "Producers reflect on profound experience walking with Indigenous artists on country". ABC News. Archived from the original on 31 January 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- ^ "Australian Aboriginal flag". City of Adelaide. 13 May 2019. Archived from the original on 19 July 2019. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ Knowles, Rachael (23 May 2022). "Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Flags flank Prime Minister's debut". NITV. Archived from the original on 4 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ Mahony, Jack (28 July 2022). "Senate President Sue Lines no longer wants the Lord's Prayer read before each sitting day in Parliament". Sky News Australia. Archived from the original on 28 July 2022. Retrieved 28 July 2022.
- ^ Opie, Rebecca (27 May 2022). "Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander flags permanently fly at Government House". ABC News. Australian Broadcasting Corporation. Archived from the original on 4 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
Further reading
- Mounter, Brendan (29 May 2021). "Torres Strait Islanders fly the flag for cultural identity on banner day for community". ABC News.
- Torres Strait Islander flag (AIATSIS)
- "Torres Strait Flag". Torres Strait Regional Authority.