Tracks the position of an IMU attached to a subject's foot during walking using Python. The algorithm uses Fusion to obtain a measurement of acceleration in the Earth coordinate frame from gyroscope and accelerometer data. The measurement of acceleration is then integrated to obtain a measurement of velocity. The measurement of velocity is corrected for drift using a zero-velocity detection algorithm and then integrated to obtain the measurement of position.
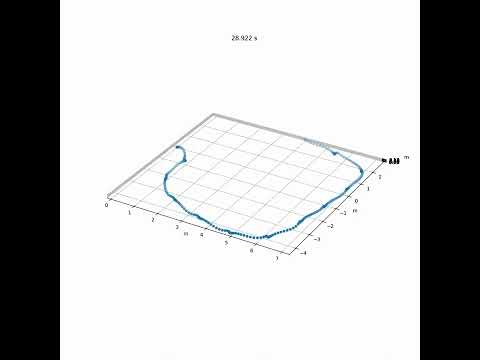
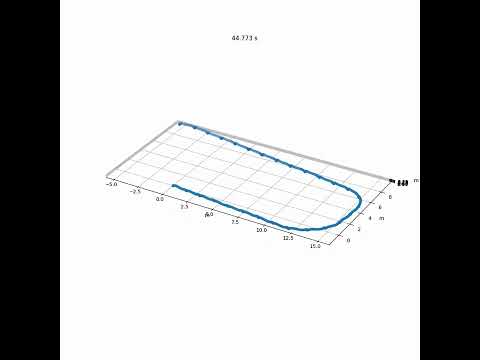
The repository includes two example datasets collected using an NGIMU. In both datasets, the subject walks in a loop so that the foot ends at the same location that it started. The accuracy, evaluated as the final displacement of the foot is 82 mm for a ~25 m walk (short_walk.csv), and 421 mm for a ~60 m walk (long_walk.csv). Animations generated for each dataset are available on YouTube and linked to below.
 |
|---|
| Gait Tracking with IMU in Python (short_walk.csv) |
 |
|---|
| Gait Tracking with IMU in Python (long_walk.csv) |